Yes. We provide flexible MOQ and fast prototyping services. Whether you need a single prototype or a small batch run, we can deliver high-precision gears within 2–3 weeks.
- support@ddgear.com
- North 3F, Building 13-2, Zhixin Park, NO.1099 Xianhua South Street, Wucheng, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China.
Drive Durable Gear
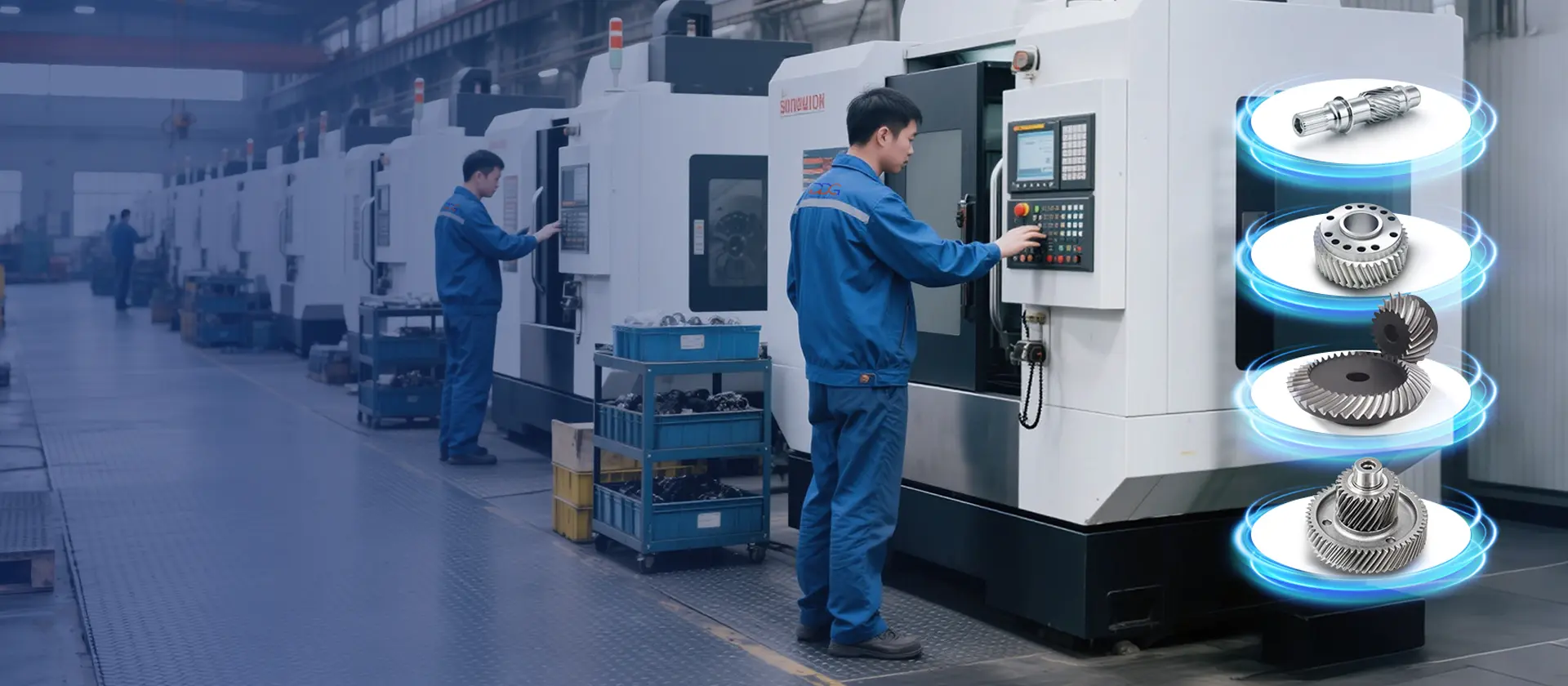
From robotics to EVs, from medical to automation — precision gears for every industry.
Reliable precision gears for robotics, automotive, and beyond.
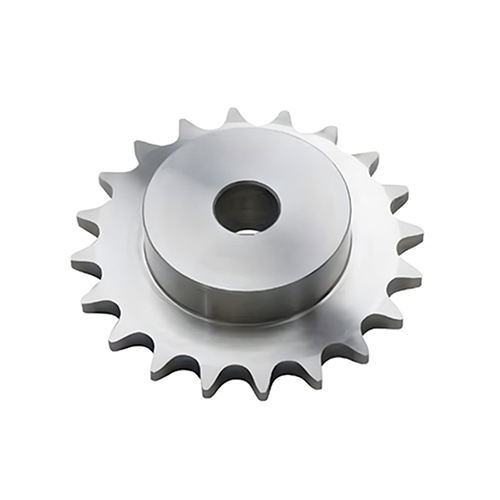
Sprockets
Sprockets are profiled wheels with teeth that mesh with roller or conveyor chains to transmit mechanical power and motion between shafts or to drive tracks and conveyors.In a typical chain drive, the driving sprocket engages the chain and pulls it around a loop; the chain then rotates a driven sprocket or moves a conveyor, providing a simple, efficient, and robust means of power transmission for machinery, vehicles, and material-handling systems.
DD Gear designs and manufactures custom sprockets for chain-driven systems in agricultural equipment, construction and material-handling machinery, automated conveyors, robotics, and other industrial applications. All sprockets are made to order based on your drawings, chain standards, and operating conditions. We focus on precision tooth profiles, controlled bore and hub tolerances, and appropriate materials and heat treatments so that each sprocket delivers reliable, low-maintenance performance in demanding environments—whether it is part of a compact robot axis or a heavy-duty conveyor line.
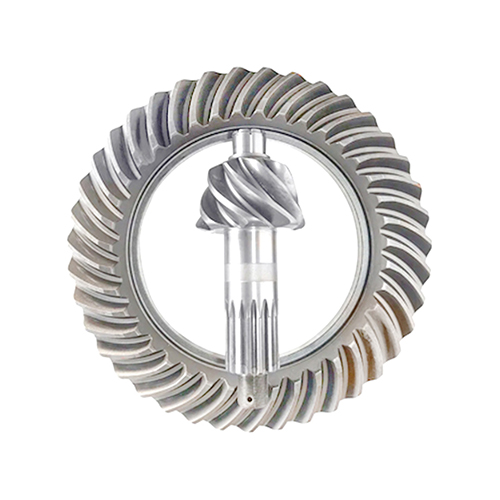
Crown Wheel and Pinion
The Crown Wheel and Pinion – Custom Differential Gear Set is the core gear pair inside an axle or final drive, also known as the ring and pinion gear set. The small pinion gear receives torque from the driveshaft, transmission, or e-motor and meshes with the larger crown wheel (ring gear). Together, they turn the drive through 90° and provide the final reduction ratio between the driveline and the wheels.By selecting the correct number of teeth on the crown wheel and pinion, the gear set simultaneously reduces speed and increases torque, adapting powertrain output to the axle load and tire size. For example, a 41-tooth ring gear driven by a 10-tooth pinion yields a 4.10:1 ratio – the pinion turns 4.1 times for each revolution of the crown wheel. In modern vehicles and off-highway machines, these gears are usually spiral bevel or hypoid designs, which offer higher torque capacity, smoother engagement, and lower noise than straight bevel gears.
DD Gear supplies custom crown wheel and pinion sets on a build-to-print basis for axles, differentials, transfer cases, and e-axles. We focus on accurate tooth geometry, controlled contact patterns, and robust materials and heat treatments so that each matched gear set delivers quiet, durable operation under high torque and cyclic loading in automotive, off-highway, and new-energy applications.
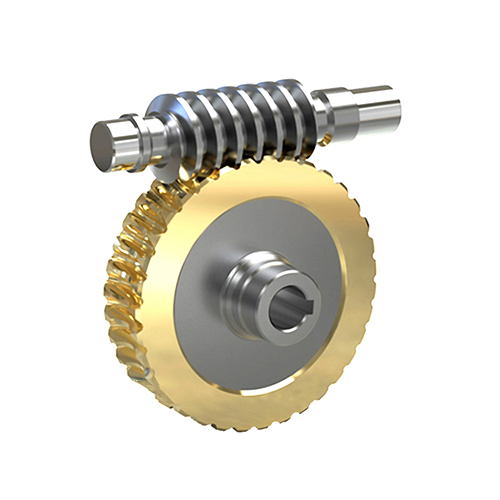
Worm Gear
A worm gear set consists of a screw-like worm meshing with a toothed worm wheel arranged at a right angle. Unlike conventional spur or helical gear pairs, the helical thread of the worm engages the teeth of the worm wheel with a sliding action, allowing the system to achieve very high reduction ratios—often up to about 100:1 in a single stage while keeping the gearbox compact.Because of the geometry and friction between the worm and wheel, many worm drives also show a self-locking effect, meaning the worm can drive the wheel but the wheel cannot back-drive the worm under normal conditions. This property, together with the high single-stage ratio, smooth operation and low noise, makes worm gears a preferred solution for hoists, elevators, conveyors, valves, actuators, steering systems and various positioning mechanisms where compact layout and load-holding capability matter.
DD Gear designs and manufactures custom worm and worm wheel sets according to customer drawings. Typical configurations use a case-hardened steel worm running against a bronze or brass worm wheel, combining strength with good wear and sliding properties. With small-module precision machining, optimized materials and heat treatment, and strict accuracy control based on international worm-gear standards, we help customers build efficient, durable, and safe worm-drive solutions for industrial machinery, automation, robotics and motion systems.
Helical Gear
The Helical Gear – Custom Helical Gear for Smooth, High-Load Transmission is a cylindrical gear whose teeth are cut at an angle to the gear axis, forming a helix around the pitch circle. Because the teeth engage gradually along the helix rather than meeting all at once, helical gears transmit torque with smoother, quieter operation and less vibration than spur gears.The inclined teeth also mean that multiple teeth are in contact at the same time, which increases tooth strength and load-carrying capacity, allowing helical gears to handle higher speeds and higher power than spur gears of the same size. With proper design and lubrication, industrial helical gearboxes can reach efficiencies in roughly the 94–99% range per stage, comparable to spur gears.
Helical gears can transmit power between parallel shafts (standard helical gear pairs) and, in crossed-axis form, between non-parallel shafts (screw gears), giving designers flexibility in gearbox layout. DD Gear focuses on small-module, high-precision helical gears produced to international accuracy standards (ISO 1328 / DIN 3961/3962). We manufacture external and internal helical gears according to customer drawings for EV transmissions, industrial gearboxes, robotics actuators, AGV drive units, and other automated machinery where quiet running, efficiency and durability are critical.
Synchronizer
A synchronizer is the friction and locking device inside a synchromesh gearbox that matches the rotational speeds of the shaft and the selected gear before their dog teeth engage. Instead of sliding gears directly into mesh—which would cause grinding when speeds differ—the synchronizer uses a small cone clutch formed by the synchronizer ring (blocker ring) and the gear’s friction cone to create friction torque and accelerate or decelerate the rotating parts. Once the speeds are close enough, the sleeve can move past the ring and lock the gear to the shaft, giving a smooth, quiet shift.A typical synchronizer unit includes a hub splined to the shaft, a sliding sleeve, one or more synchronizer rings with friction linings, and keys/springs or struts that control movement and locking force. Modern designs may use single-cone, double-cone or multi-cone arrangements to increase effective friction area and reduce shift force.
Synchronizer rings were traditionally made from brass or bronze, but many transmissions now use sintered steel, molybdenum or carbon-based friction linings to handle higher torques and improve wear life. DD Gear manufactures custom synchronizer components—primarily synchronizer rings, mating cones and related precision parts—according to customer drawings for truck, bus, passenger-car and off-highway gearboxes, including conventional MT and AMT/DCT platforms. Our focus is tight control of cone geometry, friction surfaces and tooth accuracy so each component supports reliable, comfortable gear shifting over the full transmission life.
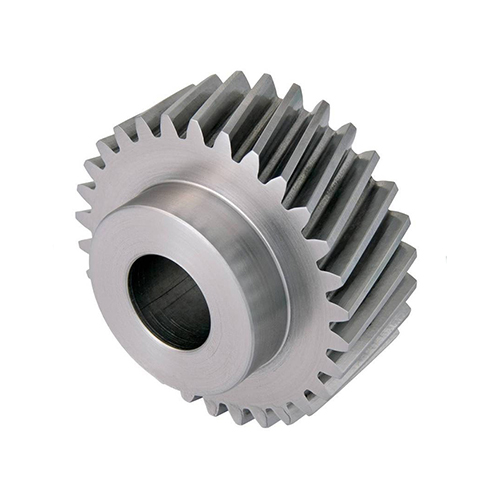
Spur Gear
The Spur Gear – Custom Spur Gear for Efficient Power Transmission is a cylindrical gear with straight teeth cut parallel to the gear axis. Spur gears are the most common and fundamental gear type used to transmit motion and power between parallel shafts in mechanical systems. Their simple geometry makes them easy to design and manufacture while delivering a precise, constant speed ratio between driving and driven shafts.Because spur gears operate primarily with rolling contact along the tooth profile and have no helix angle, they can achieve very high mechanical efficiency—typically in the 94–99% range for well-designed meshes—making them one of the most efficient gear types for moderate ratios and speeds. At higher speeds, however, the sudden engagement of straight teeth can generate more noise and vibration than helical gears, so spur gears are generally preferred for moderate-speed, cost-sensitive, and compact parallel-shaft applications.
DD Gear manufactures custom spur gears according to customer drawings, focusing on small-module, high-precision components for EV transmissions, robotics, AGVs, medical devices, machine tools, and other automated equipment. With accuracy controlled under international cylindrical gear standards such as ISO 1328 and related DIN/AGMA systems, we provide spur gears that combine high efficiency, consistent accuracy and robust durability in demanding applications.
Shaft
A shaft is a rotating machine element that transmits power and torque from one location to another and supports rotating components such as gears, pulleys, sprockets and couplings. In powertrain systems, transmission shafts are subjected to combined torsion and bending from gear forces, chain or belt loads, and their own weight, so they must be designed for fatigue strength and stiffness over long service lives.DD Gear focuses on custom transmission shafts and gear shafts produced to customer drawings. These include input shafts, output shafts, gear shafts with integral gears, spline shafts and intermediate shafts used in EV drives, truck and off-highway gearboxes, industrial gearboxes, AGV drive units and automation equipment. Typical designs use forged alloy steels such as 42CrMo4 / AISI 4140 / SCM440 and related grades, which are widely used for heavily loaded shafts due to their strength and toughness.
Shaft performance depends not only on material and heat treatment, but also on accurate bearing seats, fits and runout. DD Gear machines shaft journals, shoulders, splines and gear seats to tight tolerances based on ISO 286 fits for holes and shafts, helping customers achieve stable alignment, low vibration and long bearing and gear life. With small-module precision gearing capability inside the same plant, we can also supply integrated gear-shaft components, reducing assembly interfaces and improving concentricity.
Bevel Gear
The Bevel Gear – Custom Bevel & Hypoid Gears for Angular Power Transmission is used to transmit motion and torque between intersecting or crossing shafts, typically arranged at a right angle. Bevel gears have teeth formed on the surface of a truncated cone, allowing power to “turn a corner” while maintaining a defined speed ratio.According to international standards such as ISO 23509, the term “bevel gears” includes straight bevel, spiral bevel, zerol bevel and hypoid gears. Straight bevel gears have straight teeth and are widely used where speeds and noise requirements are moderate, while spiral bevel gears use curved teeth to provide more gradual engagement, higher contact ratio and greater load capacity. Hypoid bevel gears, with offset axes, are commonly applied in automotive differentials and drive axles to handle high torque with smooth operation.
DD Gear designs and manufactures custom bevel and hypoid gear sets based on customer drawings and specifications. Typical applications include automotive and EV differentials, steering systems, right-angle gearboxes for machinery, robotic joints and AGV drive axles, where compact angular transmission, efficiency and durability are essential. Geometry is designed in line with ISO 23509 and related bevel gear standards, while accuracy follows recognized systems such as DIN 3965 and the ISO bevel gear accuracy tables published via AGMA/ISO. With DD Gear’s focus on small-module precision gearing for emerging industries, we help customers build reliable angular drives with consistent contact patterns and long service life
PRECISION THAT DRIVES THE FUTURE
Immerse yourself in the world of high-precision gears engineered for robotics, EVs, and intelligent automation. From humanoid robots to advanced electric vehicles, DDGear provides customized gear solutions that combine accuracy, durability, and quiet performance.
We are committed to innovation and reliability — every gear we produce is designed to make our customers’ assembly easier, systems more efficient, and operations more stable.
- 15+ Years of gear manufacturing experience
- 30+ Countries served worldwide
- 4 Grade Accuracy or better in precision standards
- 2–3 Weeks fast prototype delivery



Years of Gear Manufacturing

Technology Patent

Staff

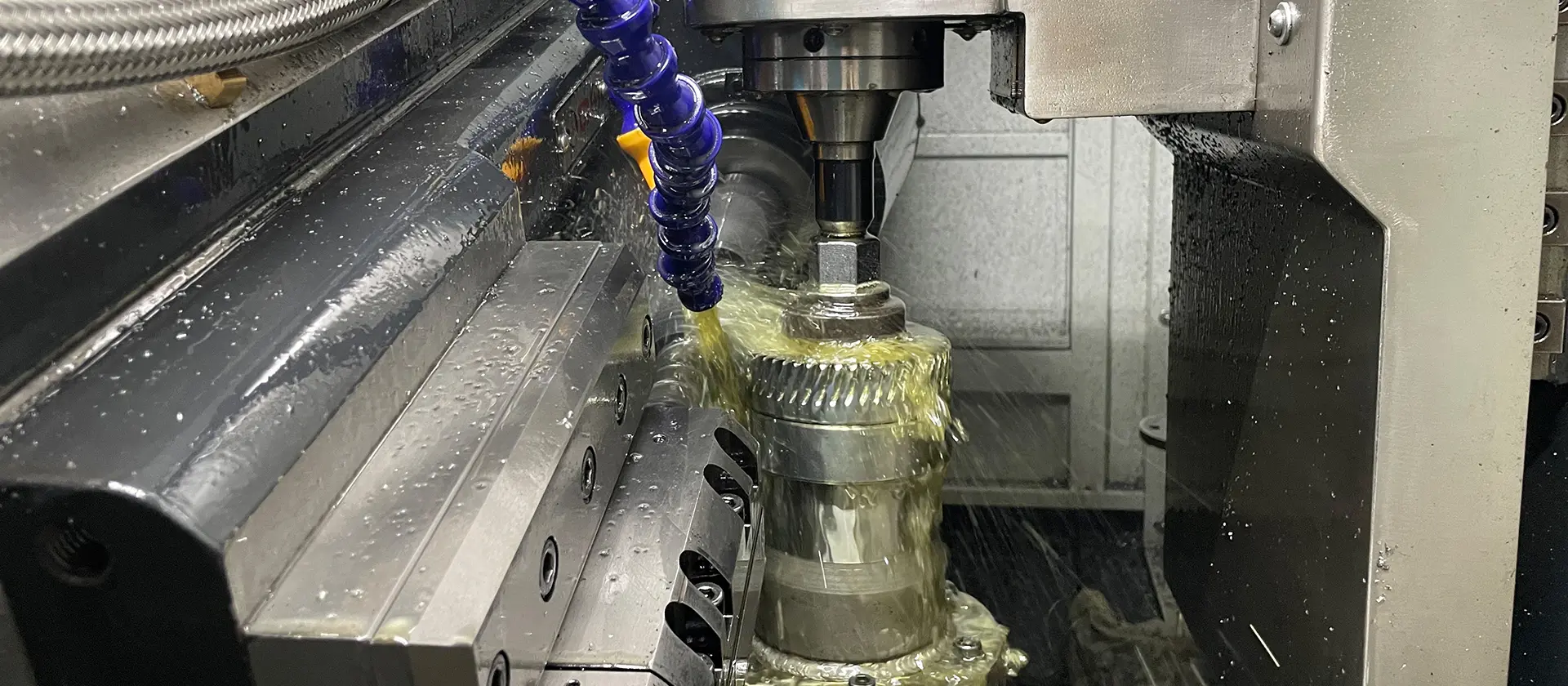
CNC & Gear Machining
Precision gears that empower robotics, EVs, and advanced machinery worldwide.
EV Gear – Custom Helical Reduction Gears for Passenger EV Drive Unit
Case Highlights
A new-energy vehicle OEM was developing a front-drive e-axle for a C-segment passenger EV. The original prototype reducer used standard helical gears, but whine noise at highway speeds and mesh efficiency were not yet at target.
DD Gear delivered a two-stage small-module helical gear set with optimized micro-geometry and case-hardening steel (18CrNiMo7-6), a material widely used in high-load automotive gears thanks to its strong, tough core and wear-resistant case. After tuning on DD Gear prototypes, the project achieved:
-
Quieter mesh in key speed ranges (improved interior NVH impression).
-
Higher mesh efficiency, contributing to better energy consumption. Research shows that properly optimized helical gears and surface finishing are essential for high-efficiency EV reducers.
Customer Background & Project Scope
-
Customer industry: New-energy passenger vehicle OEM.
-
Application: Single e-axle with a two-stage helical reduction between a high-speed PMSM traction motor and the differential.
-
Target vehicle: Front-wheel-drive compact EV used for city and highway commuting.
-
Key requirements:
-
High efficiency over WLTP-type drive cycles.
-
Very low gearbox whine, because EVs lack engine masking; tonal gear noise is easily heard.
-
Consistent quality at automotive mass-production volumes.
-
The OEM’s baseline design already used helical gears, but gear micro-geometry, material grade and grinding needed to be improved to meet aggressive NVH and durability targets.
Challenges
-
Gear whine around cruising speeds
-
Interior tests showed noticeable tonal noise from the reducer at typical mesh frequencies during 80–110 km/h cruising.
-
Even though helical gears inherently run smoother and quieter than spur gears, transmission error (TE) and manufacturing deviations can still excite annoying tones in EVs.
-
-
Efficiency & thermal performance
-
The reducer needed better mesh efficiency to support competitive kWh/100 km figures.
-
Literature indicates that finely ground or polished helical gear flanks and optimized micro-geometry are key to reducing losses and avoiding micropitting in EV gearboxes.
-
-
Durability at high speed & torque
-
High input speed and peak torque demanded a deep case-hardened alloy steel with good core toughness. 18CrNiMo7-6 / 17CrNiMo6 case-hardening steels are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial and automotive gears for this reason.
-
DD Gear Solution
1. Helical Gear Design & Micro-Geometry
-
Two-stage helical layout
-
Maintained the overall ratio requested by the OEM, but adjusted tooth counts and helix angles to improve contact ratio and mesh kinematics.
-
Helical gears are preferred in EV transmissions because gradual tooth engagement reduces impact, vibration and noise compared with spur gears.
-
-
Multi-objective micro-geometry optimization
-
Applied profile and lead modifications (crowning, end-relief) based on contact and dynamic simulations to minimize loaded transmission error over the main torque/speed window. Similar studies show that careful tooth modification is an effective method to reduce vibration and noise in helical gear transmissions.
-
Focused on those gear pairs contributing most to audible whine, following EV transmission noise analysis practices.
-
2. Materials & Heat Treatment
-
Case-hardening steel
-
Selected 18CrNiMo7-6 for high-load gears; this case-hardening steel offers excellent surface hardness, core strength and toughness for gears and shafts in demanding transmissions.
-
Case depth and hardness were specified to match the OEM’s load spectrum.
-
-
Heat treatment & finishing
-
Carburizing + quenching followed by fine gear grinding; grinding is recommended in EV gear design guidelines to achieve high efficiency and reduce micropitting risk.
-
Surface finishes were tuned to support low-viscosity oils used for efficiency in modern EV transmissions.
-
3. Manufacturing & Gear Accuracy
-
ISO 1328 accuracy
-
Tooth profile, helix deviation and pitch controlled to ISO 1328 Grade 4–5, a high accuracy class suitable for low-noise, high-speed helical gears.
-
-
Process control
-
SPC on critical dimensions, flank deviations and runout.
-
Routine gear-pair tests for TE, loaded contact pattern, and backlash before release.
-
Results
After adopting the DD Gear gearset and running multiple prototype loops:
-
NVH
-
Interior measurements showed significant reduction in tonal gear noise in the previously critical speed bands.
-
The cabin sound profile became more dominated by road and wind noise, which is the typical design goal for refined EVs.
-
-
Efficiency & thermal behavior
-
Bench tests indicated a measurable improvement in reducer efficiency (in line with studies that show optimized helical gear design and finishing can boost efficiency).
-
Temperature rise of the gearbox oil under steady-state highway operation was reduced compared with the baseline design.
-
-
Durability & robustness
-
Endurance testing under the OEM’s duty cycles showed stable contact pattern and no early micropitting or scuffing in the test window.
-
The OEM approved the DD Gear design for SOP and listed DD Gear as a key gear supplier for this EV program.
-
Typical Technical Specifications
Representative; DD Gear customizes parameters for each EV platform.
| Item | Parameter |
| Gear Layout | Two-stage small-module helical reduction |
| Power Range | ~80–150 kW traction motor (program-dependent |
| Gear Ratio | Overall i ≈ 8–12 (per OEM design) |
| Module Range | m 1.5–3.5 (helical) |
| Material | 18CrNiMo7-6 / similar case-hardening steels |
| Surface Hardness | Case-hardened, high hardness with tough core |
| Accuracy Grade | ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 |
Case Summary
By combining high-grade case-hardening steel, EV-oriented helical gear micro-geometry, and ISO Grade 4–5 gear accuracy, DD Gear helped this EV OEM:
-
Reduce gear whine and tonal noise in the e-axle.
-
Improve mesh efficiency and thermal behavior under real driving cycles.
-
Validate a robust, series-production gearset for its new EV platform.
This approach is suitable for passenger EVs, hybrid drive units and light commercial EVs that demand high efficiency and low NVH.
Developing a new e-axle, motor reducer or auxiliary EV drive?
Contact DD Gear’s engineers to co-design small-module helical gears that balance efficiency, NVH and durability.
Medical Equipment Gear – Driving Accuracy in High-End Devices
Case Highlights
A European medical-equipment OEM needed very quiet, precise motion in its imaging systems: patient table drives and positioning axes near the scanner gantry. Existing gears caused noticeable noise and slight motion ripple, which could affect patient comfort and positioning repeatability.
DD Gear supplied small-module helical and bevel gears with low-noise geometry and, for MRI-adjacent modules, options in non-magnetic materials. The new gearsets delivered smoother motion, lower sound levels near the patient, and more stable positioning, while fitting into the OEM’s existing drive layout. Medical imaging and diagnostic devices generally require smooth, quiet components to avoid disturbing patients and to protect image quality.
Customer Background & Project Scope
-
Customer industry: European manufacturer of imaging and diagnostic systems (CT / angiography / X-ray tables; some MRI-adjacent equipment).
-
Application:
-
Horizontal and vertical motion of patient tables.
-
Rotary and linear positioning of imaging heads or detector modules.
-
-
Key requirements:
-
Quiet operation close to patients, in line with hospital noise expectations. High-contact-ratio helical gears are often used to meet hospital noise requirements.
-
Smooth, backlash-controlled motion to avoid image artifacts and re-scans.
-
For MRI-adjacent axes, low-magnetic or non-magnetic material options (aluminum, bronze, austenitic stainless, etc.).
-
The OEM’s legacy drives used a mix of standard steel spur/helical gears. As systems evolved toward higher resolution and more patient-friendly environments, noise and micro-vibration became limiting factors.
Challenges
-
Noise and patient comfort
-
During table movement and gantry positioning, sound pressure near the patient couch was higher than the OEM’s new target.
-
Tonal gear noise was particularly noticeable in quiet imaging rooms, where background noise is low and patients may already be anxious.
-
Smoothness & positioning repeatability
-
Existing gears showed small but measurable backlash growth over time, leading to micro-steps in motion at low speeds.
-
For fine positioning during imaging, this could risk slight misalignment and occasional re-scans.
-
MRI-adjacent material constraints
-
For modules near MRI rooms or using shared design blocks, the OEM requested options using non-magnetic metals (aluminum, bronze, austenitic stainless steels), which are commonly used for MRI-compatible components.
DD Gear Solution
1. Gear Design & Layout
-
Small-module helical gears for quiet axes
-
Replaced selected spur gears with small-module helical gears of higher contact ratio. Helical gears are widely used in medical motion systems and medical pumps because their gradual tooth engagement reduces impact and noise.
-
Applied profile and lead modifications to minimize loaded transmission error and to keep motion smooth at low speed.
-
-
Helical / bevel combinations for space-constrained drives
-
Where right-angle motion was required (e.g., compact table columns), DD Gear used small-module bevel or spiral-bevel gears matched to a helical stage, similar to solutions seen in high-precision medical reduction gearboxes.
-
-
Backlash tuning for positioning axes
-
Controlled backlash windows to maintain table and detector positioning repeatability while allowing safe operation under temperature changes.
-
2. Materials & Heat Treatment
-
Standard medical axes (non-MRI)
-
Primary gearsets in alloy steels (e.g., 16MnCr5 / 20CrMnTi) with carburizing + grinding in high-load axes, and nitriding for lower-load, high-precision stages where low distortion is critical.
-
Gas/plasma nitriding is commonly used for precision components because it enhances surface hardness with minimal distortion, preserving tight tolerances.
-
-
MRI-adjacent options
-
Where magnetic fields or MR-conditional constraints applied, DD Gear proposed gearsets in non-magnetic metals such as aluminum bronze, brass, or austenitic stainless steels, consistent with MRI-compatible component guidelines.
-
Surface hardening methods were selected to balance wear resistance with low distortion and corrosion performance.
-
3. Manufacturing & Quality Control
-
Fine pitch & small-module machining
-
Modules in the m 0.5–2.0 range, with tight profile and lead tolerances.
-
Precision hobbing and grinding to achieve high flank quality and low roughness, which is essential for quiet, smooth motion in medical devices.
-
-
Accuracy & inspection
-
Target accuracy ISO / DIN Grade 4–6 depending on axis criticality, in line with typical high-precision medical/robotic reduction gears.
-
100% check of critical dimensions, plus sampling of tooth form, runout and backlash on a CNC gear measuring machine.
-
For selected units, assembled drives were noise-tested at medical room-like conditions.
-
Results
-
Noise & comfort
-
Measurements near the patient table showed a clear reduction in operating noise (several dB lower in key speed ranges), making motion less intrusive in the imaging room.
-
Subjectively, motion sounded softer and more “electric-motor-like”, consistent with the quiet operation that high-precision gears can bring to medical devices.
-
-
Smooth motion & positioning
-
Improved backlash control and smoother torque transfer reduced small steps and micro-vibration at low speeds.
-
Imaging engineers reported more stable positioning and fewer motion-related artifacts, reducing the likelihood of re-scans.
-
-
MRI compatibility & design reuse
-
For MRI-adjacent axes, the OEM could use non-magnetic gear options sharing the same basic geometry as standard metal versions, simplifying design reuse across product families while meeting MRI-safe / MRI-conditional requirements.
-
-
Integration
-
DD Gear’s gearsets were designed as drop-in replacements, so the OEM kept its existing housings and motor layouts, reducing project risk and implementation time.
-
Typical Technical Specifications
Representative; DD Gear customizes to each device and axis.
| Item | Parameter |
| Gear Types | Small-module helical / bevel / spiral-bevel gears |
| Module Range | m 0.5–2.0 |
| Materials | Alloy steel (carburized / nitrided); bronze; austenitic stainless |
| Surface Hardness | Up to ~HRC 58–62 (carburized) / high HV nitrided surfaces |
| Accuracy Grade | ISO / DIN 4–6 |
| Treatments | Carburizing + grinding; gas / plasma nitriding (low distortion) |
Case Summary
By combining low-noise helical and bevel designs, low-distortion surface treatments, and MRI-compatible material options, DD Gear helped this medical-equipment OEM:
-
Lower noise levels and improve patient comfort near imaging systems.
-
Achieve smoother, more precise positioning motion with stable backlash over time.
-
Reuse a common gear architecture across standard and MRI-adjacent equipment.
This approach is ideal for imaging systems, diagnostic tables, medical robots, and other precision medical devices that require quiet, accurate, and reliable gear drives.
Designing a new imaging table, diagnostic device or medical robot drive?
Contact DD Gear’s engineers to develop quiet, small-module precision gears tailored to your medical application and regulatory needs.
Humanoid Robot Gear – Low-Backlash Joint Gears for Stable Motion
Case Highlights
A Korean startup developing a bipedal humanoid robot needed very precise, low-backlash joint drives for hips, knees, shoulders, and elbows. Early prototypes used off-the-shelf gearboxes that left too much backlash and torsional compliance, making balance control and smooth walking difficult. Backlash is widely recognized as one of the most critical error sources in robot joints.
DD Gear engineered small-module spur and helical gears for the joint actuators’ internal reducers (planetary + right-angle stages). Combined with the customer’s strain-wave final stage, the upgraded gearsets delivered lower backlash, higher torsional stiffness, and smoother motion, helping the robot achieve more stable walking and arm trajectories. High-precision, low-backlash planetary and strain-wave reducers are standard in modern robotics and humanoid joints.
Customer Background & Project Scope
-
Customer industry: Korean startup focusing on humanoid robots for logistics and R&D.
-
Application: Integrated joint actuators combining a frameless torque motor, multi-stage gear reducer and encoder—similar to common humanoid joint modules that use zero-backlash precision gears and high-resolution encoders.
-
Joints covered: Hip pitch/roll, knee, ankle, shoulder and elbow.
-
Project goals:
-
Reduce mechanical backlash and increase torsional stiffness to stabilize balance and foot placement. Backlash and stiffness strongly influence motion accuracy and stability in robotic joints.
-
Keep actuators compact and lightweight for whole-body dynamics.
-
Support fast prototype iterations (small batches, 2–3 week sample lead time).
-
Challenges
-
Backlash causing wobble and tracking errors
-
Early drives used standard low-cost planetary gearheads with several arc-minutes of backlash.
-
When the robot shifted weight or swung its arms, control commands were partially “lost” in the mechanical play; the robot swayed and required frequent controller retuning.
-
-
Limited torsional stiffness in joint train
-
Under dynamic walking and push-recovery tests, joints twisted more than expected.
-
Insufficient stiffness in the gear stages amplified oscillations at the extremities—an issue also highlighted in recent research on robot joint stiffness.
-
-
Small-module, high-accuracy gears needed
-
Joint actuators relied on small-diameter, small-module gears to fit within compact housings.
-
The customer needed ISO Grade 4–5 level accuracy on key gears, similar to other high-precision robotics applications where ISO 1328 Grade 4–6 is used to minimize vibration and wear.
-
DD Gear Solution
1. Joint Reducer Gear Design
-
Low-backlash planetary & spur/helical gearsets
-
DD Gear co-designed small-module sun, planet and ring gears for the first reduction stage, targeting very low backlash when assembled with the startup’s preloaded bearings.
-
A compact helical or bevel stage was used where right-angle layouts were required (e.g., hip roll joints), similar to precision robotic gear reducers that combine planetary and bevel stages.
-
-
Micro-geometry tuning
-
Applied profile and lead modifications so multiple teeth share the load evenly and to minimize loaded transmission error, an approach widely used to improve smoothness and reduce noise in precision gearboxes.
-
Target backlash at the planetary output was kept within a few arc-minutes, so that, after the strain-wave final stage, overall joint backlash was close to the near-zero levels typical of high-end humanoid joints.
-
2. Materials & Heat Treatment
-
Carburizing alloy steels for high torque density
-
Selected 20MnCr5 / 18CrNiMo7-6 case-hardening steels for sun and planet gears—steels widely used in high-load planetary and robotic gear applications because they combine deep case hardness with a tough core.
-
Case depth tuned (~0.8–1.2 mm) for high contact fatigue strength without excessive distortion.
-
-
Heat treatment & finishing
-
Carburizing + quenching followed by precision gear grinding on critical gears to reach ISO 4–5 flank accuracy and low roughness—key for low noise, high efficiency and long life in robotics gearboxes.
-
3. Manufacturing & Quality Control
-
Small-module precision capabilities
-
Modules in the m 0.5–1.5 range machined using dedicated small-module hobbing and shaping processes; similar machines are marketed specifically for robot small-module gears.
-
-
Inspection & testing
-
100% check of key dimensions; sampling of tooth profile, helix deviation, and runout on a CNC gear measuring center.
-
Paired gearsets tested for backlash and torque transmission; assembled joint prototypes tested for torsional stiffness and lost motion before shipment.
-
Results
After integrating DD Gear’s components into its joint actuators, the startup reported:
-
Lower backlash & improved stiffness
-
Measured joint lost motion significantly reduced, bringing behavior close to the near-zero backlash levels achieved by precision planetary and strain-wave systems used in advanced humanoid and collaborative robots.
-
Increased torsional stiffness at the joints reduced oscillations at the robot’s extremities, improving positional accuracy and stability.
-
-
More stable walking & smoother manipulation
-
Balance controller tuning became easier; the robot showed less sway during single-support phases and better recovery under pushes.
-
Arm trajectories became smoother with fewer overshoot corrections, which matched the team’s expectations from high-precision, low-backlash drives.
-
-
Fast iteration & scalability
-
DD Gear supplied small prototype batches in 2–3 weeks, enabling the startup to iterate mechanical and control designs quickly.
-
The same gear families are now used across multiple joint sizes (hip vs. wrist), simplifying BOM and future volume scaling.
-
Typical Technical Specifications
Representative for humanoid hip/knee/shoulder joints; DD Gear customizes per project.
| Item | Parameter |
| Gear Types | Small-module spur / helical / planetary gears |
| Module Range | m 0.5–1.5 |
| Materials | 20MnCr5, 18CrNiMo7-6 case-hardening steels |
| Case Depth | ~0.8–1.2 mm |
| Surface Hardness | HRC 58–62 (case), tough core for shock loads |
| Accuracy Grade | ISO / DIN 4–5 on critical gears |
Case Summary
By combining small-module high-accuracy gears, low-backlash planetary stages, and EV-grade case-hardening steels, DD Gear helped this humanoid-robot startup:
-
Cut joint backlash and raise torsional stiffness, enabling more stable walking and manipulation.
-
Maintain compact actuator size while increasing torque capacity and durability.
-
Iterate fast from prototype to pilot builds with reliable small-batch production.
This approach is ideal for humanoid robots, collaborative arms, service robots and exoskeletons that need compact, precise, and durable joint gear solutions.
Working on humanoid or advanced robotic joints?
Contact DD Gear’s engineers to co-develop small-module, low-backlash gearsets tailored to your joint actuators.
Exploring The Science of Precision Gears
Quality Control in Precision Gear Manufacturing
Introduction Quality control is the backbone of precision gear manufacturing. For gears used in demanding applications such as robotics and EVs, consistent reliability is ensured only through a rigorous quality management system spanning design, production, and delivery. 1.Design Stage Control From profile optimization to material selection, all design elements are evaluated to ensure manufacturability, durability, and performance. 2.Process Control Real-time monitoring, statistical process control (SPC), and automated inspections are applied throughout machining to minimize deviations and maintain tolerances. 3.Final Inspection Profile and lead measurement Noise and vibration testing Endurance and wear verification These checks ensure that every gear meets both functional and quality standards. 4.Certifications & Standards Precision gears comply with global standards such as ISO 1328, DIN, and AGMA. Certified systems like ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 ensure consistent quality for international customers. Conclusion Strict quality control guarantees not only the accuracy and durability of precision gears but also builds long-term customer trust. By adhering to the highest global standards, precision gear manufacturers support the reliability of next-generation robotics, EVs, and intelligent automation.
Manufacturing Process of Precision Gears
Introduction Precision gears are not just the result of design excellence—they are the outcome of meticulous manufacturing. Every stage, from raw material to final inspection, determines the gear’s performance, durability, and accuracy. 1.Blank Preparation Gear blanks are typically made from forgings, castings, or bar stock. Material quality is the first guarantee of gear reliability. 2.Gear Cutting Hobbing: High efficiency, suitable for mass production. Shaping: Ideal for internal gears and complex profiles. Shaving: Improves tooth surface finish and precision. 3.Heat Treatment Processes such as carburizing, nitriding, and induction hardening are applied to enhance hardness, wear resistance, and durability. 4.Finishing Grinding: Achieves sub-micron tolerances. Polishing: Reduces roughness, minimizes noise. Finishing operations ensure smooth performance and precise accuracy. 5.Inspection & Testing Gears undergo profile and lead measurement, noise analysis, and endurance testing to guarantee consistent performance. Conclusion Manufacturing precision gears is a blend of science, engineering, and craftsmanship. By strictly controlling every process, manufacturers can deliver gears that meet the demanding standards of robotics, EVs, and industrial automation.
Application Fields of Small-Module Precision Gears
Introduction In today’s high-tech industries, gears remain at the heart of power transmission. Small-module precision gears, with their compact size and high accuracy, have become essential components in robotics, electric vehicles, medical devices, and automated logistics. Robotics Small-module gears are widely used in humanoid robot joints, collaborative robots, and industrial robots. They provide high-precision rotation and torque transfer in limited spaces, ensuring smooth and repeatable movements. Electric Vehicles In EV drive motors and two-speed gearboxes, small-module gears enable high-speed operation with low noise, improving energy efficiency and driving comfort. Medical Devices Medical devices demand stability and quiet operation. Small-module gears are applied in surgical robots, imaging equipment, and precision delivery systems. Automation & AGVs In AGVs and automated warehousing, small-module gears power lifting mechanisms and steering wheels, ensuring efficient and reliable material handling. Conclusion Small-module precision gears are driving the future of industries, providing a solid transmission foundation for next-generation robots, EVs, and intelligent systems

Customized precision gears for you
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
From robotics to electric vehicles, you'll find clear answers to every question here, and our engineering team will design, prototype, and deliver the perfect gear solution for you.
-
Do you support small-volume custom orders?
-
What industries are your precision gears mainly used in?
Our gears are widely applied in humanoid robots, electric vehicles, AGVs, industrial automation, and medical devices. We also provide tailored solutions for specific customer applications.
-
How do you ensure the precision and quality of your gears?
We strictly follow international standards such as ISO 1328, DIN, and AGMA. With advanced CNC and gear grinding equipment, plus full inspection systems, we guarantee ≤ Grade 4 accuracy, long durability, and consistent performance.


IATF16949 Approved
Please fill out the form below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.